Billing - A Complete Beginners Guide
Billing - A Complete Beginner's Guide
Billing has remained one of the top priorities for Service Providers. As varied and innovative Services are offered to Customers, it has become more imperative to generate correct and accurate charges.
Services can be Data browsing, Gaming, Streaming, OTTs, Voice, Text, API exposures, and Partner services like Netflix, HBO Go, etc.
Billing (be it for Telecom/SaaS/XaaS/Utility/etc.) is the process of accurately accounting for the Services consumption.
Through billing, Service Providers calculate and generate bills for the services offered. This includes collecting all kinds of Charges (One-time, Recurring & Usage), Rating billable events, handling Disputes/Adjustments, Taxation, Discounting, Payments, Invoicing, etc.
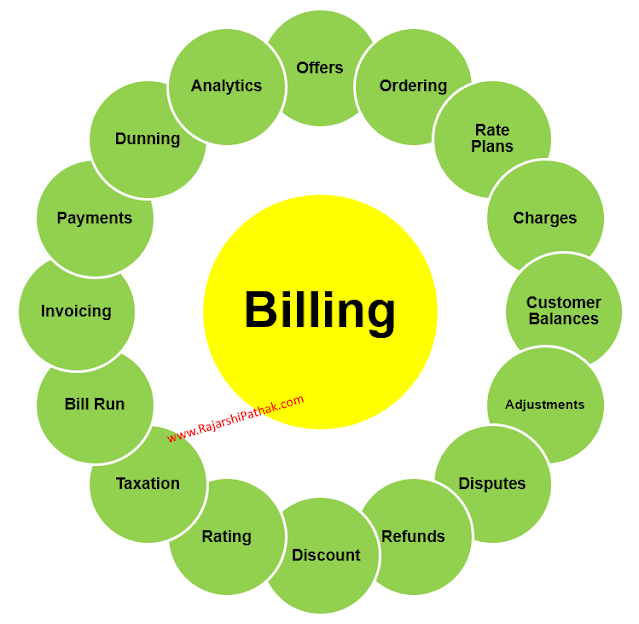 |
| Billing Overview |
There are two ways to charge customers - Prepaid and Postpaid.
Prepaid involves customers paying in advance for the use of services. In a pre-paid system, customers purchase a Voucher or Credit, which is then used to pay for services as they are used. Once the credit or validity is exhausted, customers need to recharge their accounts to continue using the services. Bills are not generated for Prepaid Customers.
This charging mechanism is targeted at low ARPU customers and covers services like Pay-per-views (PPVs), Speed boost, Extra GBs, etc.
Postpaid involves customers using services first and paying for them later. In a post-paid system, customers are billed for the services they have used during a specific billing period, which is typically a month.
Bill Run is performed for Postpaid customers and a Payment inquiry is raised against the Invoice. Customers are required to pay the bill within the Payment due date, failing which leads to Dunning actions.
Postpaid mechanism is targeted at high ARPU customers who have maintained creditworthiness and generally show more stickiness to the Service Providers.
Subscription Services like Postpaid Mobile, Broadband, Pay TV, Gaming, IoT Agricultural Sensors, etc. are billed through it.
Essential Elements of a Billing System:-
Measuring Service Usage: The first step is to collect usage data from the Network. This data can be collected from a variety of sources, including Usage Events (or CDRs) which contain information, such as the start/end time, data consumption, call duration, A Number, B Number, Location, Supplementary services used, Trunk ID, etc.
For Offline Charging, Mediation is used for collecting, processing, enriching & distributing events to the Rating Engine.
For Online Charging, AAA activities are handled by using protocols like CAMEL, RADIUS, Diameter, HTTP/2, etc. between Network elements and OCS. Rated events are also stored for further processing during the Bill Run.
Customers can view their own consumed usage through the Self-service Portal and make changes to their service plans.
Rating Engine: Billable events are rated by Rating Engine. It converts the Service Consumption into Charges.
Price or Rate plans define the charges for different types of services. For example, per API exposure, per Minute, per GB, etc. along with the unit of the measurement. Rating Engine supports complex pricing plans, such as peak and off-peak, Tiered, Volume-based, Overage, etc.
The billing system uses rated events to calculate charges based on the customer's service plan. Along with the Usage events, the Rating Engine also processes One-Time and Recurring billable events.
Billing Engine: Billing Engine generates bills based on the charges calculated by the Rating engine. It also manages the billing cycles, payment due dates, and payment reminders.
The billing system must be able to handle a variety of different payment methods along with a variety of different billing cycles. For example, some customers may be billed on a monthly basis, while others may be billed on a quarterly basis.
Bill Run takes care of activities like handling deferred actions, creating bills, collecting credit card/direct debit payments, generating refunds, creating invoices, etc.
Billing Cycle consists of Billing Frequency and Billing Day of the Month (BDOM).
Billing Frequency determines how often to bill the customer and request payments. Billing Frequency can be Monthly, Semi-Annually, Annually, etc.
Billing DOM determines when to finalize the bill. For example, Customer gets billed on the 5th of every month.
Before the actual bill run, many Operators execute Trial Bill Run to verify the accuracy of the bill extracts. Once verified, the bill extracts go to bill formatting & printing.
The detailed steps related to Trial Bill Run are shown below:
 |
| Trial Bill Run |
Invoicing: The final step is to generate invoices. Invoices capture the charges for the consumed services that have been used.
Invoices are typically sent to customers on a monthly basis. Invoices are delivered via paper bills, emails, or online self-care portals.
The invoice includes a detailed breakdown of the services used, charges applied, applicable discounts, taxes, and any applicable promotional messages.
The overall processing of Charges (One-Time, Recurring, and Usage) by Rating Engine is shown below, including Bill Run and Invoice Generation:
 |
| Processing Charges, Rating, Bill Run, and Invoice Generation |
Payments: Service Providers offer various Payment methods to facilitate payment against the Invoice or Services used.
Different Payment methods are Credit/Debit Cards, Bank Transfers, Online Platforms like Apple Pay, Google Pay, Cash, Cheques, Vouchers, etc.
As explained earlier, Customers need to Pay first (mostly by Vouchers or Online recharge) to utilize Prepaid Services and Pay later against the Invoice for utilizing Postpaid Services.
Payment processing involves the collection of payments from customers and the reconciliation of payments with the bills generated.
Collections/Dunning: If a customer does not pay their bill within the Payment due date, Service Providers may send them a dunning notice.
The non-payment of bills then leads to triggering dunning actions like Suspending services, Barring outgoing calls, Terminating services, Agent recovery, Write-offs, etc.
Collections/Dunning actions vary based on the Credit Class of the Customer. For High-Risk Customers, actions will be quicker and more stringent & as compared to Low-Risk Customers.
Self-Serve Portal: Customers can view their billing information, make payments, and create Trouble tickets via Self-Serve Portals.
Other Scenarios:
- In a Parent-Child Account hierarchy, the non-paying Child's bill amount gets rolled up to the Parent. Parent Account needs to pay the consolidated bill.
- Sometimes after the Invoice generation/dispatch, the Customer raises valid disputes against which the Operators need to generate adjustments to the bill. In such cases, the Provider may generate Corrective Bills/Invoices for the Customers.
- One Customer Account can have multiple Subscriptions related to different Services. Billing System should be able to generate a consolidated & itemized bill for all the Subscriptions. Invoices are normally dispatched to the "Bill To" address.
- Incase the bill amount balance due is quite minimal, the Operator may decide to suppress the bill generation. The current customer charges (including taxes) can be rolled over to the next bill run. Taxes, if any, need to be paid by the Operator to the Authorities.
- When it comes to Bill Run, Operator can decide to run it every day or on specific days of the Month (e.g. 1, 5, 10, 15...), depending upon the billable customer population. Some Operators divide the Customers into different Segments and execute the bill runs based on Segments. This way also, they can handle the bill processing without overloading their BSS systems.
I will cover several other Billing scenarios in my upcoming articles.
Billing System To Consider:
Accurate billing and simplified invoices play a crucial role in improving Customer Retention and loyalty. Service providers must ensure that their billing systems are accurate and reliable. Any errors in the billing process can lead to customer dissatisfaction and lost revenue.
Billing System needs to be secured to protect Customers and Payment related information.
At the same time, Billing needs to be scalable to handle the increased volume of transactions. Operators can use cloud-based solutions to store and process data. This can help to reduce the cost of billing and rating and improve the scalability & reliability of the billing and rating process.
Service providers must comply with various regulatory requirements, such as taxation and data protection laws. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in legal issues. Operators can work with regulators to understand the regulations that govern the billing and rating process. This can help to ensure that the billing and rating process is compliant with the regulations. For example, in many regions, it is mandatory to generate Invoices or Notifications in the local language.
With Customer focus & improved experience in mind, Billing models are shifting towards Personalization in terms of better Offer choices, flexible payment terms, attractive discounting, multi-currency, loyalty management, bundling, and so on.
Service Providers need to ensure the timely resolution of all customer bill inquiries and complaints.
As the Telecom & other industries like Utility, Media, etc. continue to evolve, billing will remain an essential component for the Service Providers.
--------------
Kindly share this article with your friends and colleagues. Feel free to like and comment. Happy learning.
Glossary: BSS (Business Support Systems), BDOM (Billing Day of the Month), AAA (Authentication, Authorization, Accounting), PPV (Pay Per View), OCS (Online Charging Server)









Post a Comment