IMS is a service framework
to deliver multimedia services over IP Networks. It is predominantly used for
delivering interactive services like Voice, IP Centrex Service, Video chat, Video
Conferencing, and Instant Messaging-based multimedia services (VoNR, VoLTE,
VoWiFi, RCS, etc.).
As IMS is access-independent, it is quite relevant in
5G Networks.
It connects to the
5G SBA for delivering services like Voice over 5G (VoNR or Vo5G) and allows
roaming features over 5G/4G networks.
To know more about how traditional IMS
(used for 4G/WiMAX network) needs to be evolved for a Cloud-based 5G SA Network,
please check my other article by clicking on the link.
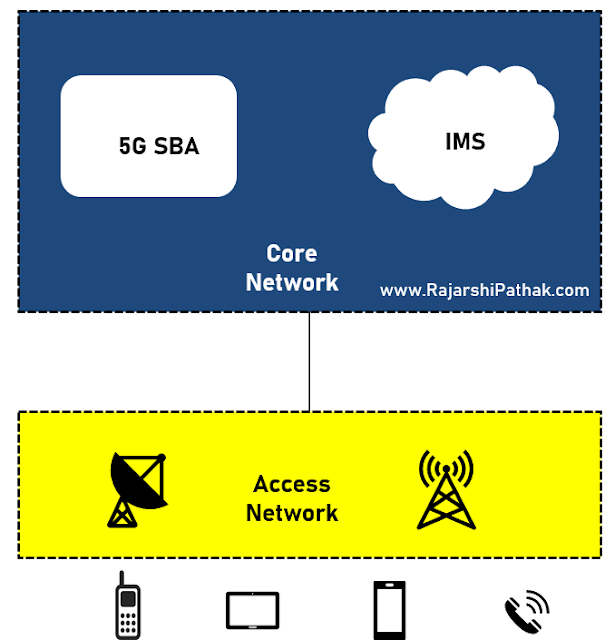 |
| IMS in a 5G Network |
Let’s discuss some of the important IMS
Nodes –
P-CSCF/I-CSCF/S-CSCF: These IMS nodes are used for Voice
session control and call routing. Handling of user registration and service authorization
has also been taken care of via CSCFs.
AS/AF: Executes Telephony, IDDs, Supplementary
services, and several multimedia services like Video calls, Video conferencing,
etc.
MRF: Handles media processing, media
streams (like announcements), media stream mixing, etc.
MGCF: Takes care of Signaling interworking
between legacy networks (PSTN/PLMN) and IMS network, that is, ISUP to SIP
conversions. It also takes care of controlling the resources of MGW.
BGCF: It is used during call routing to
PSTN/PLMN networks. From a protocol perspective, it handles SIP as well as SS7.
IMS-GWF: Enables online charging in S-CSCF for
IMS services like voice calls, video chats, etc.
HSS: Maintains Subscriber’s user profiles
in the home network and helps to manage user identification.
Let’s delve into IMS in a 5G Network –
 |
| IMS Service Access in a 5G Network |
For any Non-IMS terminating call, IMS detects the B-Party
as an Off-net subscriber and forwards the SIP signaling message to MGCF via
BGCF. SIP messages get converted to ISUP and reach PLMN via MGW. Later, Bearer
gets established between IMS and non-IMS users through the MGW node.
For IMS to IMS On-net calls, the call arrives in the IMS
server (comprised of P-CSCF, I-CSCF, and S-CSCF). IMS server interacts with AS
incase of any supplementary services initiation. IMS server forwards SIP signaling messages to the B-party within the network. Once the call is
connected, a Bearer path gets established between both the IMS users.
IMS allows maintaining QoS for Service types and Subscriptions based on its integration with PCF/PCRF. Not only it allows call
control within the IMS network, but it also connects calls to legacy/non-IMS
networks.
A typical Voice session in a 5G Network
is shown below –
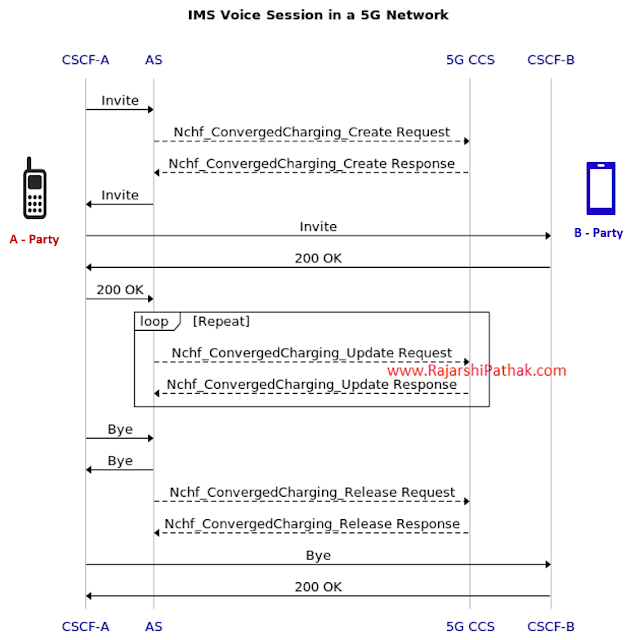 |
| IMS Voice Session in a 5G Network |
IMS nodes communicate in SIP protocol whereas 5G CCS
understands HTTP/2 Rest APIs.
CSCFs and AS perform the authentication & service
authorization by interacting with 5G CCS. On sufficient balance or available credit
limit, call signaling gets established with the B-Party. Once the Voice session
gets established, subsequent balance checks & reservations occur using Nchf
Update requests/responses. As the call terminates, with a successful Nchf Release
request/response, the actual balance update happens over the Customer account.
Here, Nchf is the Network Function Service-based
interface with Converged Charging Function.
IMS nodes must be deployed over the cloud like other 5G Core network functions like AMF, SMF, etc.
Through Service Control over SIP, IMS can manage parallel services. From a Charging perspective, it supports
Offline Charging, Online Charging, Flow-based Charging, etc.
Along with standard Services, as mentioned at the
beginning of the article, it facilitates IDD (International Direct Dialing),
Supplementary services like Call Forwarding, Missed Call Notifications, Call
Barring, Speed Dialing, CLIP/CLIR, Multi-party Calling, Call Waiting,
Voicemail, etc.
Please refer to my article for further details about 5G Service-based Architecture and various 5G Network functions.
Glossary: IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem), SBA (5G Service Based
Architecture), SIP (Session Initiation Protocol), SS7 (Signaling System 7), CSCF
(Call Session Control Function), P-CSCF (Proxy CSCF), S-CSCF (Serving CSCF),
I-CSCF (Interrogating CSCF), ISUP (ISDN User Part), HSS (Home Subscriber
Server), MRF (Media Resource Function), MGCF (Media Gateway Control Function),
BGCF (Breakout Gateway Control Function), SGW (Serving Gateway), PGW (Packet
Gateway), AMF (Access Management Function), SMF (Session Management Function),
UPF (User Plane Function), UDM (Unified Data Management), IMS-GWF (IMS Gateway
Function), PCF (Policy Control Function), PCRF (Policy & Charging Rules
Function), CCS (Convergent Charging Server), ABMF (Account Balance Management
Function), RF (Rating Function), CGF (Charging Gateway Function), CHF (CHarging
Function), VoLTE (Voice over LTE), VoWiFi (Voice over WiFi), RCS (Rich
Communication Services), VoNR (Voice over New Radio), 5G SA (5G Standalone
Architecture), CLIP (Calling Line Identification Presentation), CLIR (Calling
Line Identification Restriction), IDD (International Direct Dialing), PLMN
(Public Land Mobile Network), PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network)












Post a Comment